Tuesday, 24 December 2024
How the Universe forms the Golden Ratio in organic and inorganic matter
Sunday, 22 December 2024
Quantum Mechanical Mass mechanism ~ Why Mass increases
Friday, 13 December 2024
Origin of the Fine Structure Constant 137 revelled for the first time
Video on the Fine Structure Constant or Coupling Constant.
An amateur in a theory called ‘Dyslexic Artist Theory on the Physics of
Time’ explains one of the greatest mysteries of physics the Fine Structure
Constant 137 or Coupling Constant.
This Theory explains a process of energy exchange that is formed by the spontaneous absorption and emission of light photon ∆E=hf energy, therefore the Fine Structure Constant 137 is linked to the speed of light or what is called the light constant c. Within the electron sphere 4πr² that surrounds the atomic nucleus.
The Fine Structure Constant is also linked to the charge of the electron e² squared and the Planck constant h/2π. These three constants form the Fine Structure Constant within a dynamic geometrical process.
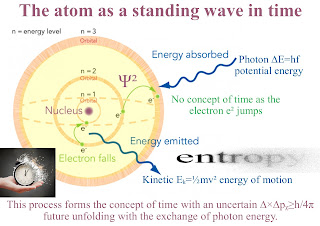
Diagram of a Photon electron coupling or Dipole Moment. This spontaneous process forms the characteristics of three-dimensional space and continuum of time ∆E ∆t ≥ h/2π.
Tuesday, 10 December 2024
Why Infinite Number of Calculation Explained Geometrically, no Renormalization in Feynman's QED
In this theory, the
mathematics of Quantum Mechanics represents the physics of time with Classical
physics representing processes over a ‘period of time’ as in Newton’s
differential equations.
This idea is supported by the fact that photon ∆E=hf energy is continuously transforming potential energy into the kinetic Eₖ=½mv² energy of matter in the form of electrons.