I would like to dedicate this video on Hodgkin and
Huxley model of Neurons.
That basically explains Neurons as electric circuits with the organization and movement of positive and negative charge. The positive and negative is in the form of ion atoms.
The neuron membrane acts as a boundary separating
charge with ionic gates embedded in the cell membrane forming the potential for
the build-up and movement of ion charge.
This process
can form signals along the neurons with the potential difference across the
cell membrane forming what is called an action potential.
To answer
this question we have to look deeper into the process.
When we do this, we find that the movement or
action of charged particles like ions emit photon ∆E=hf energy.
Therefore, this whole process can be based on an
interpretation of Quantum Mechanics
In the
theory explained in these videos, Quantum Mechanics represents the physics of
time ∆E ∆t ≥ h/2π as a physical process.
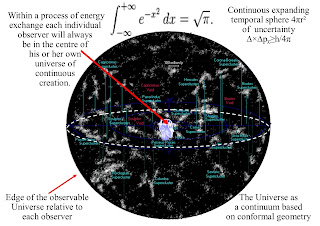
We have a probabilistic uncertain future coming
into existence with the absorption and emission of light with potential energy
PE continuously transformed into kinetic Eₖ=½mv² energy of electrons as an
uncertain ∆×∆pᵪ≥h/4π future comes into existence with each photon ∆E=hf electron
interaction.
With each photon electron interaction, a potential
future is emitted as a wave of probability with the past being annihilated in
the form of anti-matter annihilation.
Because light has momentum and momentum is frame dependent,
we can place each individual life form in the centre of their own reference frame
in the moment of now.
References:
There Are Biophotons in the Brain. Is Something
Light-Based Going On?
Neurons in the human brain produce photons, and are
apparently capable of being the infrastructure for light-based communication
and activity:
https://bigthink.com/mind-brain/there-are-biophotons-in-the-brain-is-something-light-based-going-on/
Photons guided by axons may enable
backpropagation-based learning in the brain:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-24871-6
Neurons Unexpectedly Encode Information in the
Timing of Their Firing
A temporal pattern of activity observed in human brains
may explain how we can learn so quickly:
https://www.quantamagazine.org/a-new-kind-of-information-coding-seen-in-the-human-brain-20210707/
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0254152
Department
of Mathematical Sciences
B12412: Computational Neuroscience and
Neuroinformatics
The Hodgkin-Huxley model
https://www.maths.nottingham.ac.uk/plp/pmzsc/cnn/CNN3B.pdf
Introduction to Spiking Neural Networks: From a
Computational Neuroscience perspective
What
physicists refer to as photons, other people might just call light. As quanta
of light, photons are the smallest possible packets of electromagnetic energy:
https://www.symmetrymagazine.org/article/what-is-a-photon?language_content_entity=und
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photon
Schematic diagram outlining the potential modes of
biophoton network communication and repair among neurons. If a neuron is very
active or damaged (i.e., the biophoton neuron), its mitochondria may
communicate with other neurons (the bystander neurons) through either axonal
pathways and resulting synapse or through the extracellular matrix. The
biophoton neuron, if damaged, may also use biophotons to repair itself and
bystander neurons. Neurons that are not linked synaptically to the biophoton
neuron nor in a surrounding region (through extracellular matrix) would remain
unaffected (the unaffected neuron). Note that biophotons have a broad range of
wavelengths, from ultraviolet to red to infrared:












No comments:
Post a Comment